Basic Data Types In C++ [C++ Tutorials – 4]

C Plus Plus Basic Data Types
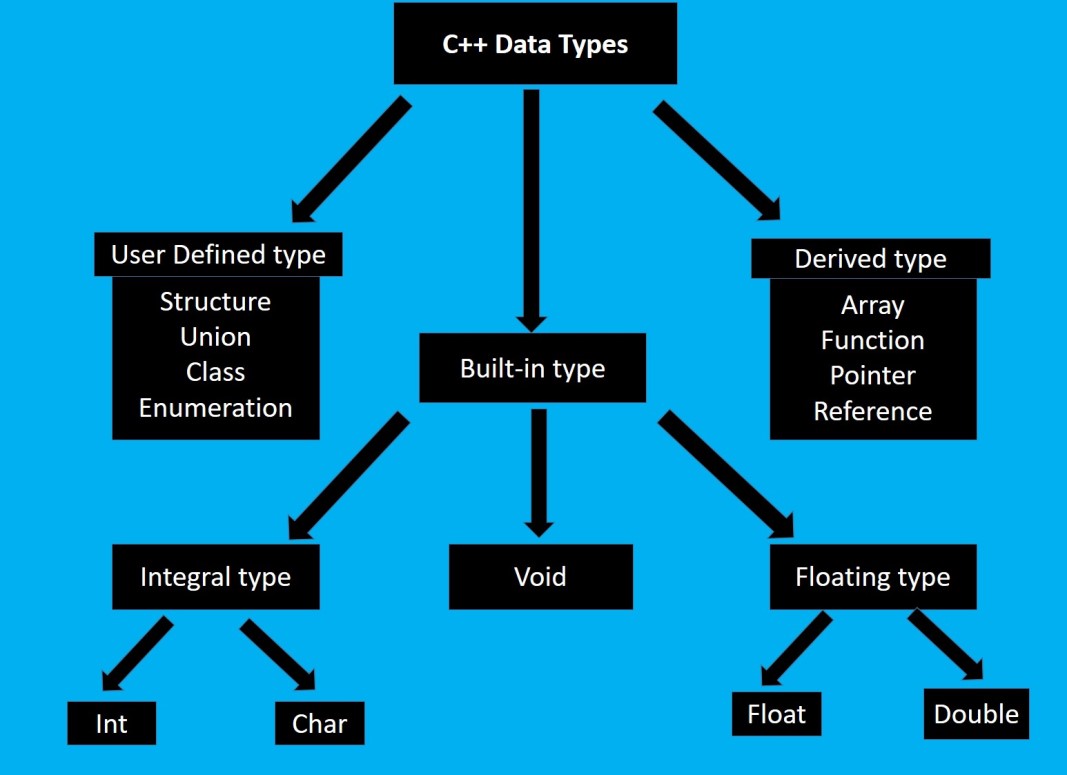
Data types in C++ are means to identify the type of data. C++ data types can be classified as follows.
Fundamental Data Types
Fundamental data types are also known as atomic data types. These data types are built-in data types of C++ and are not composed of other data types. In C++ there is five type of fundamental data types which are described below.
1. int: An identifier declared as int becomes an integer type variable and can hold integer values such as 1, 34, 100 etc.
eg: int x;
2. char: An identifier declared as char becomes a character variable which can store any number of the C++ basic character set. It os often said to be integer type because of letters, symbols etc. are represented internally in memory by integers ranging from 0 to 255.
eg: char name;
3. float: An identifier declared as float becomes a floating point variable and can hold numbers having a fractional part.
eg: float avg;
4. double: It stands for double precision floating point. It stores floating numbers with much larger range and precision as shown in the figure given below.
5. void: The void type specifies an empty set of values. It is used as the return type for functions that do not return a value.
|
Type |
Approximate Size (in type) |
Minimal Range |
|
short unsigned short signed short |
2
2 2 |
-32768 to 32767 0 – 65,535 -32768 to 32767 |
|
int unsigned int signed int |
2
2 2 |
-32768 to 32767 0 – 65,535 -32768 to 32767 |
|
long unsigned long signed long |
4
4 4 |
-2147483,648 to 2,147,483,647 0 to 4294,967,295 -2147483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| char
unsigned char signed char |
1 1 1 |
-128 to 177 0 – 255 -128 to 177 |
|
float double long double |
4 8 10 |
3.4 x 10-38 to 3.4 x 1038-1
1.7 x 10-308 to 1.7 x 10308-1 3.4 x 10-4932 to 3.4 x 104932-1 |
Derived Data Types
Derived data types are secondary datatypes which are formed by deriving from the fundamental data types. C++ supports the following derived data types.
Arrays:
An array refers to a named list of a finite number of similar data elements. Each of the data elements can be referenced respectively by a set of consecutive numbers 0,1, 2, . . . , n.
Assume that we have an array of five elements which is named as student; then its elements will be referred to as student[1], student[2], . . . student[4].
An array can be single dimensional or multi dimensional.
Syntax:
type array_name [size];
Eg:
int student[5];
I will describe more about arrays in later discussions.
Functions
A function is a set of statements that can be processed independently. Every C++ program must consist of at least one function which is called the main function.
Syntax
type function_name (argument type);
Eg:
int total (int,int);
I will describe more about functions in later posts.
User Defined Data Types
Structure
A structure is a group of related data types referenced by a single name. The keyword struct is used to declare a structure.
Syntax:
struct structure_name
{
type data_item1;
type data_item2;
................
};
Eg:
struct student
{
int rollnumber;
char name[15];
char cource[15];
float persentage;
};
I will describe structure briefly in upcoming posts.
Classes
A class is used to represent a group of similar and related objects. The keyword class is used to declare classes in c++.
We will discuss more about the Classes in later discussions.